What is Dehydration?
Dehydration occurs when you lose fluids and are not replenished, meaning you’re not drinking enough water. It can occur from vomiting or diarrhea, sweating too much, or simply not drinking enough water throughout the day.
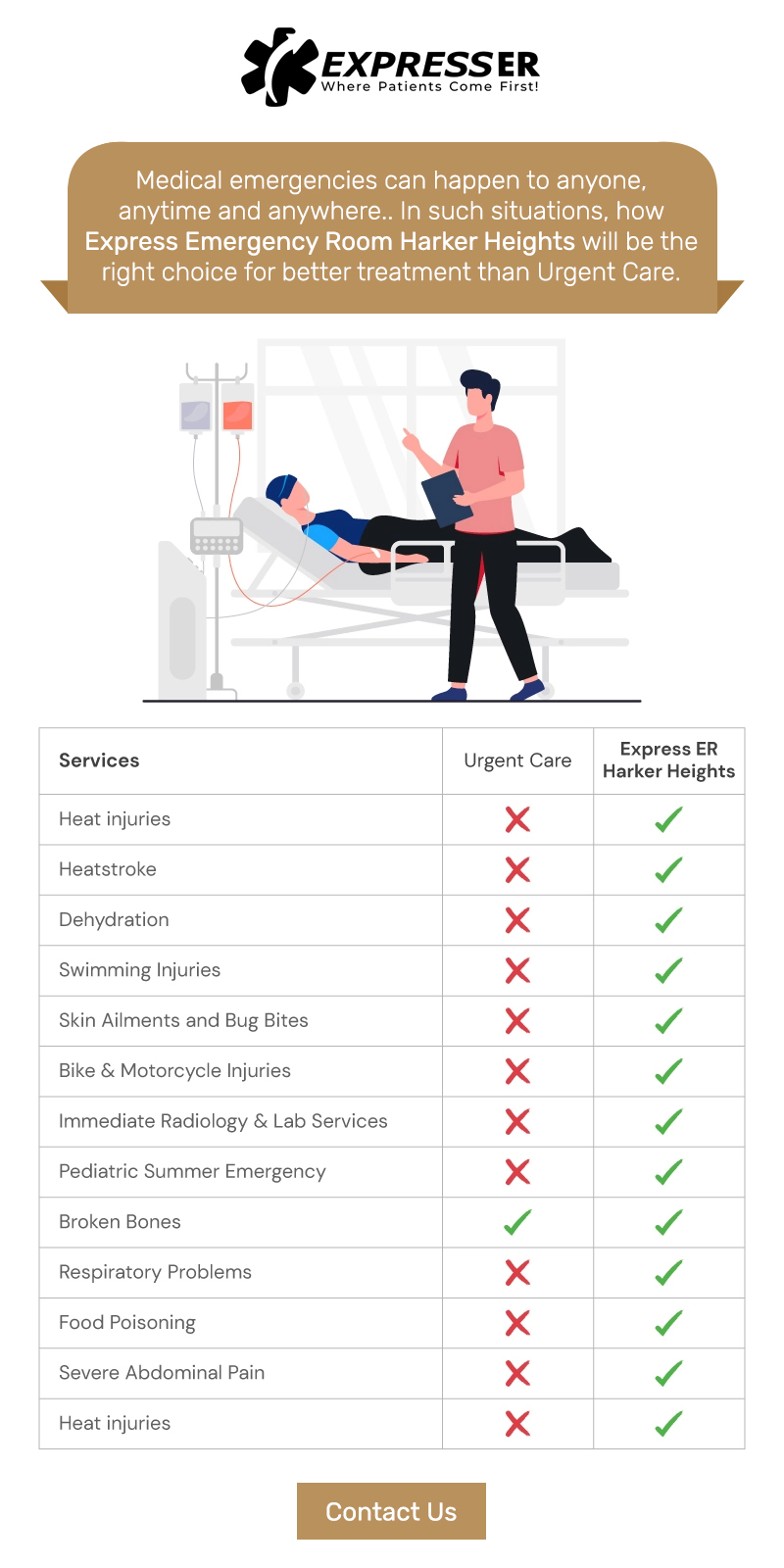
Dehydration can cause serious health concerns, including shock and organ failure. If left untreated, dehydration can cause life-threatening complications—so you must know the signs and symptoms of dehydration so you can seek immediate care.
What Causes Dehydration?
Dehydration is caused by a lack of water in your body. Water is lost through sweat, urine, and stool. Fluid loss occurs when you lose salt or other minerals through vomiting, diarrhea, or blood loss. Your body can also lose fluids by using them to digest food or because of excessive alcohol consumption.
The most common cause of dehydration is heat exhaustion. Too much exercise causes sweating, which leads to fluid loss through urination and breathing. The amount you sweat depends on how much you are exercising and how hard you are working out; it also depends on the temperature outside and whether or not there is any wind chill factor.
What are the Symptoms of Dehydration?
The symptoms of dehydration include:
- Dark urine or infrequent urination with dark urine
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Extreme thirst for fluids (inability to take in enough liquid) may cause you to drink more than usual. In healthy adults who don’t have symptoms of dehydration, extreme thirst can mean that your body water levels have decreased (but not dehydration). However, if you’re a child or elderly person who doesn’t feel well or has not passed urine in a while, it could be a sign of dehydration!
Other symptoms include:
- Dry mouth and tongue; no saliva production can lead to dry mouth.
- Fatigue/drowsiness due to lack of adequate hydration. This affects fluid flow to the body cells, causing them not to function correctly due to a lack of energy supply.
When is Dehydration an Emergency?
Dehydration can be serious and is not an easy illness to treat at home. If you have been vomiting or have had diarrhea for more than 24 hours and haven’t been able to keep liquids down, you need to go to the emergency room in Harker Heights, TX, so that your condition can be evaluated by a medical professional.
Dehydration can cause problems like reduced blood pressure, and it can make it dangerous for people with underlying health conditions like cardiovascular problems or diabetes; therefore, seeing a doctor is even more important!
Drinking water replenishes water levels. However, you can also take fruit juices or smoothies to restore the levels and lost electrolytes (sodium) in our bodies that help regulate things like muscle contractions, which our hearts need plenty of when working hard from pumping blood.
You should visit the best ER near you if you have lost a large amount of fluid in a short time and are experiencing any of these symptoms:
- Severe headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fainting or seizures.
What are the Complications of Dehydration?
The most common complication of dehydration is low blood pressure. When you are dehydrated, your body cannot produce enough fluid to keep your blood flowing properly.
Anemia is another complication of dehydration that often occurs in children and pregnant women. When you’re not taking in water, your kidneys will stop producing the right amount of erythropoietin which means your red blood cells won’t work as well, and you’ll have less oxygen in your body.
How Is Dehydration Treated?
Dehydration is treated with fluids and electrolytes. Fluids are given intravenously, through a tube inserted into a vein in the arm, or orally, through a drink. Electrolytes are given intravenously to treat severe dehydration when there is muscle weakness, confusion, or other symptoms of an electrolyte imbalance.
Take Action!
Visit Express Emergency Room Harker Heights for assistance if you experience dehydration accompanied by a severe headache.